Struggling to fall asleep or stay asleep through the night? This affects others, too.
If it’s tossing and turning or waking up in the middle of the night, sleep issues are common. Anxiety, stress, and a racing mind are often the culprits that prevent a peaceful night’s rest.
That’s where magnesium comes in. This mineral is widely known for its sleep-supportive benefits, but here’s the thing: not all magnesium supplements are the same.
So, what type of magnesium is best for sleep? Depending on the type of sleep issue you’re facing, choosing the correct form of magnesium can make a significant difference.
Let’s break down the best magnesium for sleep, how it works, and how to choose the right one for you.
How Magnesium Affects Sleep Quality

Magnesium plays a key role in calming the nervous system by regulating neurotransmitters, preventing overactive nerves, and helping you unwind before bed.
It also supports muscle relaxation by blocking calcium from entering muscle cells, reducing tension.
Additionally, magnesium boosts GABA production, a neurotransmitter that slows brain activity, preparing you for rest.
This combination of calming effects on both muscles and the brain makes magnesium highly effective at improving sleep quality, helping you fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper, more restful sleep.
Magnesium is vital for sleep quality by supporting melatonin, the hormone that regulates your sleep-wake cycle. It ensures adequate melatonin production, helping your body transition naturally into sleep.
Low magnesium levels, however, can increase stress, anxiety, and muscle tension, disrupting sleep.
Keeping magnesium levels balanced helps maintain healthy sleep cycles, leading to deeper, more restorative rest. Regular magnesium intake can be a simple yet effective way to improve overall sleep health.
Different Types of Magnesium Explained
Not all magnesium types work the same way, and choosing the right one for sleep can make all the difference. Here’s how the different types compare:
1. Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is often recommended for sleep improvement due to its high absorption rate and calming effects on the nervous system.
Why it’s beneficial: Unlike other forms, magnesium glycinate is gentle on the stomach, making it ideal for people with sensitive digestion.
How it works: It supports muscle relaxation and helps alleviate tension, which can be key for falling asleep.
Key point: Because of its effective calming properties and gentle nature on the digestive system, magnesium glycinate is one of the best magnesium forms for enhancing sleep quality.
2. Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium citrate is well absorbed by the body, providing effective muscle relaxation that can ease discomfort and support better sleep.
Why it’s beneficial: This form of magnesium helps reduce muscle cramps and spasms, promoting relaxation before bedtime.
Considerations: It’s worth noting that magnesium citrate has a mild laxative effect, which could cause digestive discomfort in those with sensitive stomachs or a tendency for diarrhea.
Key point: Magnesium citrate is great for muscle tension relief, but people with sensitive digestive systems should be cautious when using it before bed.
3. Magnesium Threonate
Magnesium threonate is unique because it can cross the blood-brain barrier, making it highly effective for brain health and cognitive function.
Why it’s beneficial: The study on the effect of Magnesium-L-threonate (Hausenblas et al., 2024) found that magnesium L-threonate can improve sleep and daily functioning.
How it works: By calming the mind and supporting brain function, magnesium threonate creates a peaceful sleep environment.
Key point: If stress or anxiety are preventing restful sleep, magnesium threonate could be a natural option to help ease the mind before bed, making it a good choice for those with mental overactivity.
4. Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide is commonly used for various magnesium needs but has lower bioavailability, meaning it isn’t absorbed as effectively by the body.
Why it’s not ideal: Due to its low absorption rate, magnesium oxide may not be as effective in improving sleep quality compared to other forms.
How it works: While magnesium oxide can still offer some benefits, it’s not the best choice for those seeking to use magnesium for better sleep.
Key point: With its lower absorption rate, magnesium oxide doesn’t offer the same sleep-promoting benefits as other magnesium forms and may not be as effective in achieving restful sleep
5. Magnesium Malate
Magnesium malate is known for its energizing and muscle-recovery properties, making it ideal for daytime use rather than promoting sleep.
Why it’s not ideal: Due to its energizing effects, magnesium malate may disrupt sleep if taken too close to bedtime, making it harder to relax and fall asleep.
How it works: While helpful for muscle recovery during the day, it’s best to avoid magnesium malate at night.
Key point: If you’re seeking to improve sleep, avoid magnesium malate in the evening, as its energizing effects could interfere with your ability to unwind and sleep.
What Magnesium is Best for Sleep Based on Your Needs
Choosing the right type of magnesium for sleep depends on your specific needs, such as relaxation, muscle tension relief, or mental calm.
| Sleep Need | Best Magnesium Type | Why It Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Stress and anxiety | Magnesium Glycinate | Calms the nervous system and helps you relax. It is also gentle on digestion. |
| Muscle tension or cramps | Magnesium Citrate | Relaxes tight muscles and eases cramps. Fast absorption can help you rest more comfortably. |
| Light or broken sleep | Magnesium Threonate | Supports mental calm and may help reduce waking during the night. It works well in the brain. |
How Much Magnesium Should You Take for Sleep
The general dosage range for magnesium to support sleep is 200-400 mg per day. It’s a good idea to start with a lower dose and adjust as needed based on how your body responds.
Taking magnesium about 30–60 minutes before bed is ideal, giving your body enough time to absorb it and begin relaxing.
Starting with a lower dose is important to avoid side effects like stomach discomfort or diarrhea. Once you know how your body reacts, you can gradually increase the dosage for optimal results.
Is Magnesium Safe for Sleep?
Magnesium is generally safe for most people, but it’s important to start with a low dose and consult a doctor if you have any health conditions or are taking prescription medications.
Possible Side Effects
Some people may notice mild side effects, especially with higher doses. These can include:
- Stomach upset
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
Starting small and increasing slowly can help reduce these issues.
Who Should Be Careful
You should talk to a doctor before taking magnesium if you:
- Have kidney problems
- Have a long-term health condition
Your body may process magnesium differently, so medical advice matters here.
Medication Interactions
Magnesium can affect how some medicines work, including:
- Certain antibiotics
- Diuretics
If you take prescription medication, it’s best to check with a healthcare provider first.
What Experts Say About Magnesium for Sleep
Magnesium is frequently mentioned as a sleep aid, with research and real-world experiences highlighting its effectiveness.
Research and Expert Opinions
A 2012 study in the Journal of Research in Medical Sciences found that magnesium supplementation (500 mg daily for eight weeks) improved sleep onset and reduced nighttime awakenings in older adults with chronic insomnia.
However, total sleep duration didn’t change significantly. Experts agree that while magnesium may help with stress- or muscle-tension-related sleep issues, its effects on deep sleep are limited.
Magnesium is safe for most people and has minimal side effects, making it a good option for mild sleep disturbances.
What Reddit Users are Saying
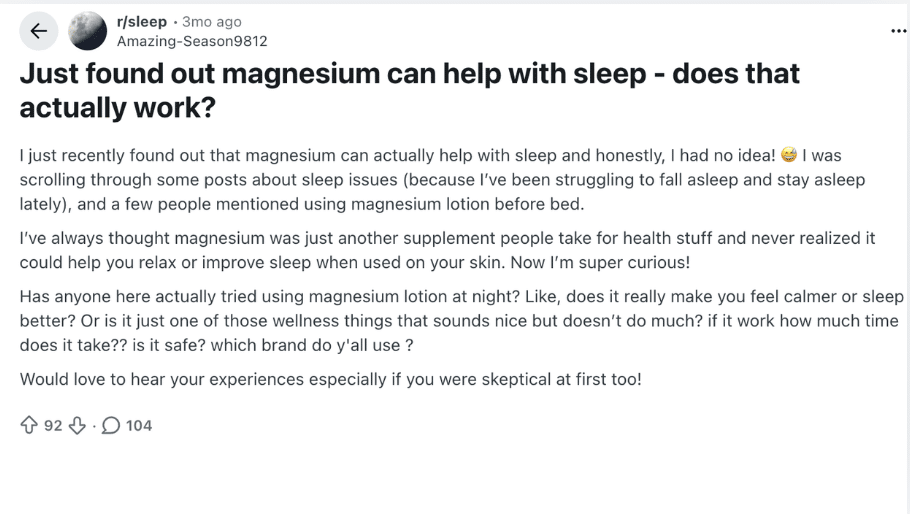
In a recent Reddit discussion, u/Amazing-Season9812 shared their curiosity about magnesium as a sleep aid, specifically magnesium lotion.
u/zac_g19 mentioned taking magnesium 45 minutes before bed to help settle in and stay asleep without grogginess.
u/MrSneller added that taking 315 mg of magnesium glycinate, along with L-theanine, significantly improved his sleep quality.
While experiences vary, many users, like u/zac_g19 and u/MrSneller, find magnesium effective for improving sleep without the morning grogginess common with other sleep aids, such as melatonin.
Magnesium Supplements vs. Magnesium from Food Sources
Choosing between food sources and supplements depends on your magnesium needs, your ability to absorb magnesium, and your lifestyle.
| Aspect | Magnesium Supplements | Magnesium Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption | Supplements provide a concentrated, easily absorbed form of magnesium. | Magnesium from food is absorbed more slowly and may require larger amounts. |
| Benefits of Sleep | Effective for those who need higher doses or are dealing with magnesium deficiency. | Food sources support general health, but may not provide enough magnesium for sleep support. |
| Examples | Magnesium glycinate, magnesium citrate, magnesium oxide | Leafy greens (spinach, kale), nuts, seeds, beans, whole grains, fish (salmon) |
Bottom Line
Magnesium plays a key role in improving sleep by supporting muscle relaxation, reducing stress, and aiding melatonin production.
By understanding the different types of magnesium, you can find what type of magnesium is best for sleep based on your specific needs.
Magnesium glycinate is often the top choice due to its calming effects and high absorption rate, but other forms, such as citrate or threonate, can be helpful depending on your needs.
Remember to start with a lower dose and consult a healthcare professional before adding magnesium to your routine.
If you’re ready to improve your sleep, try a magnesium supplement suited to your needs. For more tips on better sleep health, check out my other blogs.