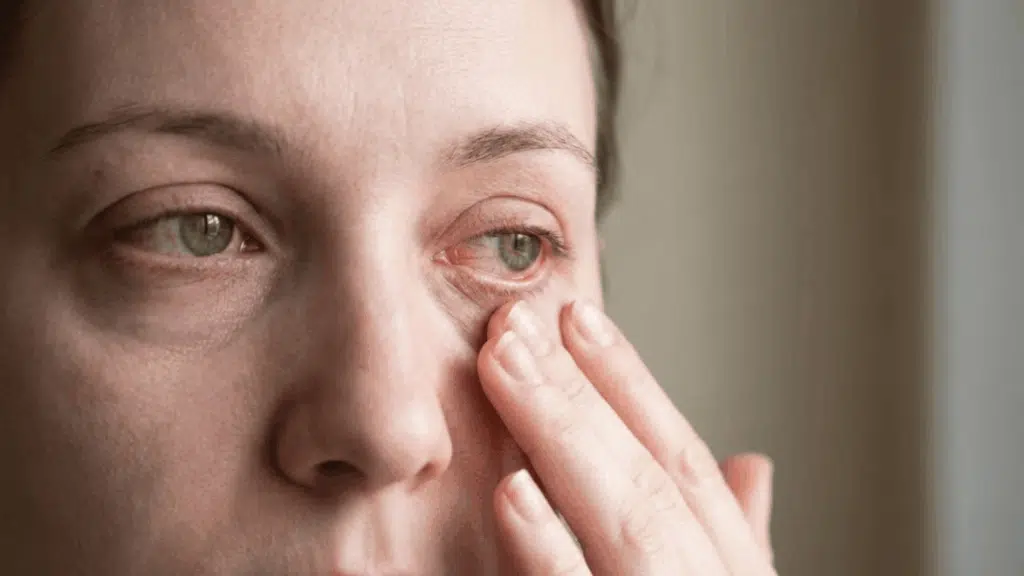
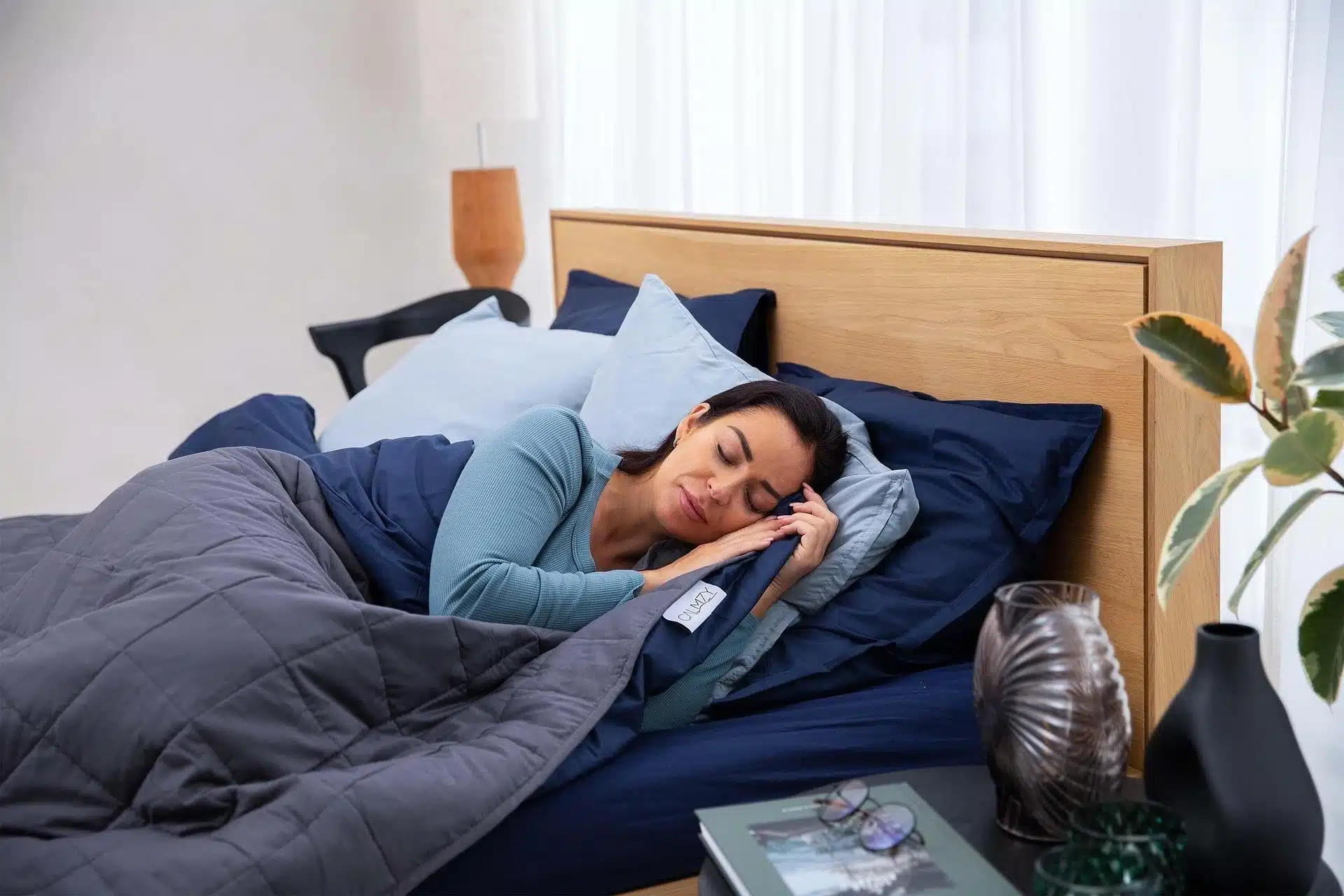
I’ll admit, I used to think skimping on sleep only made me cranky and tired. Then I started noticing my eyes feeling gritty, dry, and strangely heavy by midday.
Turns out, our eyes desperately need those nightly hours of rest to repair and refresh themselves.
When we cut sleep short, they’re among the first to protest. I’ve learned that understanding what’s happening behind the scenes can help us protect our vision and feel better overall.
Let me walk you through what I’ve found about how sleep deprivation affects our eyes and what we can actually do about it.
What Happens to Your Eyes When You Don’t Sleep?
When I miss out on quality sleep, my eyes show it almost immediately. Here’s what typically happens:
- Red or bloodshot eyes
- Dryness and that annoying gritty feeling
- Blurry vision that won’t quite clear up
- Trouble focusing on screens or text
- Eye twitching that seems to have a mind of its own
- Puffiness and dark circles that no concealer can hide
These symptoms aren’t just cosmetic annoyances. Chronic poor sleep has been linked to higher odds of developing certain eye diseases, making this more than just a temporary inconvenience.
Our eyes really do need consistent rest to function properly.
Common Eye Symptoms from Sleep Deprivation
When I skimp on sleep, my eyes rebel in predictable ways. Here’s a quick breakdown of what happens and how to recognize each symptom.
| Symptom | Why It Happens | What You’ll Notice |
|---|---|---|
| Dry, gritty, or burning eyes | Reduced tear production and unstable tear film from sleep loss | Scratchy sensation, burning feeling, eyes feel tired and heavy, worsens through the day |
| Red or bloodshot eyes and puffiness | Inflammation, poor circulation, fluid buildup, and dilated blood vessels | Visible red vessels, swollen eyelids, bags, and dark circles, puffy appearance |
| Blurry vision and focusing problems | Eye muscles and visual processing struggle without adequate rest | Intermittent blur, difficulty reading screens, trouble switching focus, headaches from strain |
| Eye twitching (myokymia) | Sleep deprivation stresses delicate eye muscles | Involuntary eyelid spasms, usually one eye, last minutes to days, resolve with rest |
Most of these symptoms improve once I return to a consistent sleep routine, but understanding what’s behind them helps me take them seriously before they become chronic issues.
The Science: How Sleep (or Lack of It) Affects Ocular Tissues

Sleep isn’t just downtime for your body. It’s when critical repair and maintenance happen at the cellular level, including in your eyes.
Here’s what research reveals about the biological impact of sleep deprivation on ocular health.
1. Tear Film, Cornea, and Epithelial Health
Sleep deprivation disrupts the ocular surface at a microscopic level. Studies show that lack of sleep causes changes to corneal epithelial cells, including alterations to microvilli structures that help maintain tear film stability.
These cellular changes lead to increased tear evaporation and reduced tear production, creating the perfect conditions for dry eye symptoms and potential surface damage.
The cornea relies on overnight rest to repair minor daily damage and maintain its protective barrier.
Read more on: Study on sleep deprivation and lacrimal system dysfunction
2. Sleep Quality and Chronic Eye Disease Risk
Growing evidence links poor sleep quality with increased risk of glaucoma and other serious eye conditions. Population studies have found associations between short sleep duration, sleep apnea, and elevated intraocular pressure.
While these associations don’t prove causation, they suggest sleep disruption may contribute to disease development or progression.
The relationship appears bidirectional, as some eye conditions also disrupt sleep quality, creating a concerning cycle that warrants further investigation and clinical attention.
Read more on: Harvard Health report on sleep and glaucoma risk
3. Brain, Attention, and Vision Function When Tired
Sleep deprivation impairs visual attention and processing speed. Research demonstrates that tired individuals experience more frequent attention lapses and microsleeps, during which visual information isn’t properly registered.
These brief lapses significantly increase the risk of accidents, particularly while driving.
The visual cortex requires adequate sleep to process information efficiently, and even mild sleep restriction can measurably slow reaction times and reduce the ability to track moving objects or respond to visual stimuli.
Read more on: CDC report on drowsy driving and impaired attention
Immediate Fixes You Can Try Tonight
When sleep deprivation starts affecting your eyes, you don’t have to wait for a full recovery to find relief. These practical strategies can help ease your symptoms right away while you work on improving your sleep.
- Use preservative-free artificial tears every 2-4 hours to combat dryness and restore moisture to your ocular surface, especially after screen time or in dry environments.
- Apply a cool compress for 10-15 minutes to reduce puffiness and soothe inflamed blood vessels around your eyes, particularly effective in the morning.
- Practice the 20-20-20 rule to reduce eye strain: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds to give your focusing muscles a break.
- Limit screen time to 1-2 hours before bed, and enable blue light filters on devices to help your eyes relax and support natural melatonin production for better sleep.
- Stay hydrated and use a humidifier to maintain moisture in the air, especially if you sleep with heating or air conditioning that dries out your eyes overnight.
- Keep your eyelids clean with warm compresses and gentle lid scrubs to prevent oil gland blockages that worsen dry eye symptoms.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes, no matter how tired they feel, as this can damage the corneal surface and worsen redness and irritation.
- Position your screen below eye level to reduce the exposed eye surface area and minimize tear evaporation during work or entertainment.
If you notice discharge, significant swelling, or if over-the-counter solutions provide no relief after several days, professional evaluation is essential to rule out underlying conditions.
Sleep Hygiene for Healthy Eyes
Establishing consistent sleep habits not only improves how you feel but also gives your eyes the nightly restoration they need to function properly.
Maintain a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, including weekends. Aim for 7-9 hours to regulate your circadian rhythm and support natural tear production cycles.
| Timing | Action | Specifics | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| After 2 PM | Avoid caffeine | No coffee, tea, or energy drinks | Prevents sleep disruption that affects eye repair |
| Before 3 PM | Limit naps | 20-30 minutes maximum | Reduces fatigue without disrupting nighttime sleep |
| 3-4 hours before bed | Skip alcohol | Avoid alcoholic beverages | Prevents dehydration and sleep fragmentation |
| 2-3 hours before bed | Finish dinner | Light meals only after this | Supports uninterrupted restorative sleep |
| 1-2 hours before bed | Start wind-down | Dim lights, meditation, light stretching | Triggers melatonin production, relaxes eye muscles |
| 30-60 min before bed | Stop all screens | Use audiobooks, podcasts, or print books instead | Eliminates blue light that suppresses melatonin |
| At bedtime | Optimize bedroom | Dark, 60-67°F, use humidifier if dry | Prevents overnight tear evaporation |
For shift workers: Use blackout shades during daytime sleep, maintain the same sleep schedule on days off, and take brief breaks during shifts to preserve your natural eye repair schedule despite irregular hours.
When Lack of Sleep is More Than Temporary: See an Eye Doctor
While occasional sleep deprivation causes temporary eye discomfort, certain symptoms require immediate professional attention.
Seek urgent care if you experience persistent eye pain, severe light sensitivity, sudden vision loss, recurring corneal erosions, double vision, or blurry vision that doesn’t improve with rest. These could indicate serious underlying conditions beyond simple fatigue.
If you’re experiencing chronic sleep problems alongside eye symptoms, the connection may run deeper. Research links poor sleep quality with increased glaucoma risk and other eye diseases.
In these cases, you may benefit from both an eye care evaluation and a sleep medicine referral to address the root cause and protect your long-term vision health.
How Sleep Deprivation Affects Special Populations?

Certain groups face heightened risks when sleep deprivation affects their eyes. If you fall into one of these categories, extra precautions and awareness can help protect your vision.
1. Contact Lens Wearers
Sleep deprivation already compromises your ocular surface, making contact lens wear riskier. When you’re tired, your eyes produce fewer tears and blink less frequently, which can create conditions for complications.
- Never sleep in lenses when exhausted, as reduced tear production and oxygen flow dramatically increase infection risk, potentially leading to serious corneal ulcers.
- Reduce wearing time on low-sleep days by switching to glasses earlier in the day to give your compromised ocular surface adequate recovery time.
- Use preservative-free rewetting drops more frequently throughout the day to compensate for unstable tear film and increased evaporation from fatigue-related incomplete blinking.
2. Shift Workers & Students
Irregular schedules and chronic sleep deprivation make you particularly vulnerable to cumulative eye damage. Proactive strategies can help minimize long-term risks.
- Schedule annual comprehensive eye exams to monitor for early signs of dry eye disease, glaucoma, or other conditions linked to disrupted circadian rhythms.
- Use blackout shades and sleep masks during daytime rest periods to support melatonin production and allow proper corneal repair despite unconventional sleep schedules.
- Take regular screen breaks during night shifts or study sessions using the 20-20-20 rule, as fatigue magnifies digital eye strain and reduces your natural blink rate.
3. People with Existing Eye Disease
If you already have glaucoma, chronic dry eye, or recent eye surgery, sleep deprivation can worsen your condition or slow healing. Close monitoring becomes essential.
- Maintain strict medication compliance even when tired, as missing doses of glaucoma drops or post-operative treatments during sleep-deprived periods can cause serious setbacks.
- Report new symptoms immediately to your eye doctor, as conditions like glaucoma can progress faster when combined with poor sleep and raised nighttime eye pressure.
- Prioritize sleep as part of treatment by discussing sleep quality with your ophthalmologist, since chronic sleep disruption may require adjustments to your management plan or additional interventions.
Final Thoughts
I never thought lack of sleep could do this much damage to my eyes until I experienced it myself. Now I understand that protecting my vision means protecting my sleep schedule.
Whether it’s the immediate discomfort of dry, red eyes or the long-term risks like glaucoma, the connection between sleep and eye health is undeniable.
If you’re struggling with how lack of sleep affects your eyes, start with small changes tonight and don’t hesitate to seek professional help when needed.
What’s your biggest challenge with sleep and eye health? Share your experience in the comments below.